Basic requirments to work in Embedded development world.
C language(0)
데이터 시트 읽는 능력(1)
- gpio(general-purpose input/output)
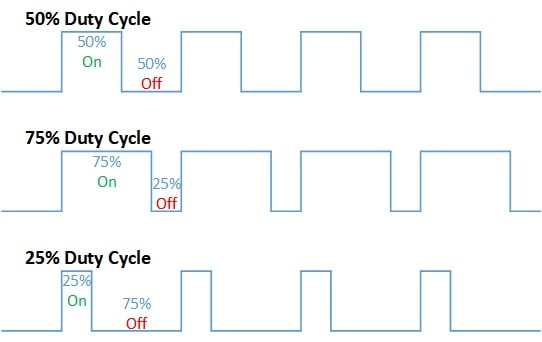
- pwm(pulse width modulation)
- make it like analog signals by differentiating ratio(duration time) of digital signals(high and low).
- Human eye cannot recognize whether LED lamp blinks or not if the frequency is over 100 Hz.
- Duty Cycle : time ratio of high and low signals, (duration time of high signal)/(duration time of low signal)
- It enables such like analog-output signal control by digital-output signals.
- Motor control could be one example, if duty ratio is going to high, velocity will be faster.
About and differences of i2c, spi, uart communications
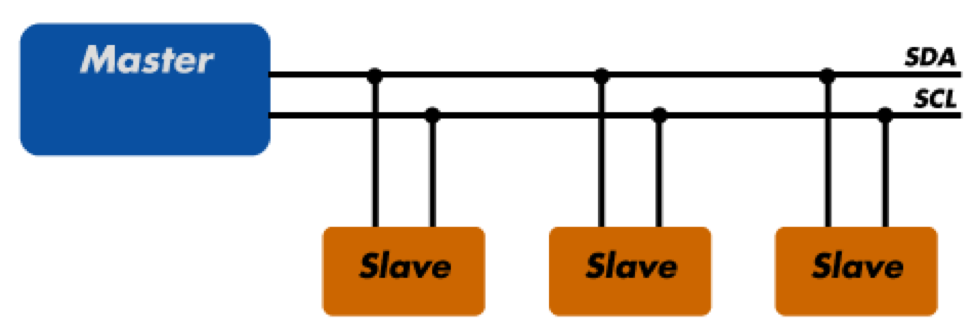
1. i2c(inter integrated circuit) :
- Half duplex mode, synchronous, low speed.
- 100 kbps(standard)
- It consists of 2 eletrical lines,
- SCL(Serial Clock) : carries clock signal
- SDA(Serial Data) : allosw master and slave to send and recieve data.
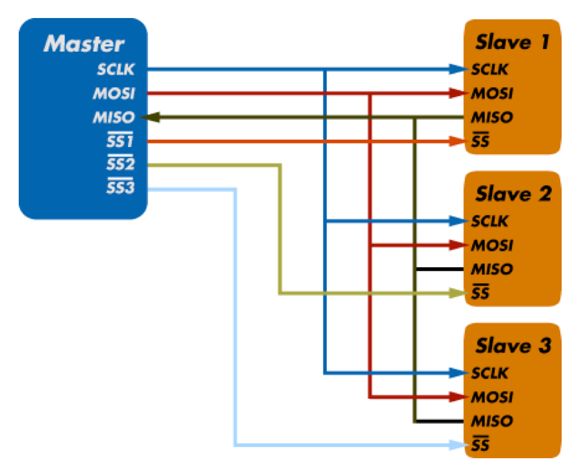
2. spi(serial peripheral interface) :
- Full duplex mode, synchronous, high speed.
- 250 Mbps @ .1m
- It has 4 lines.
- MOSI(Master Out, Slave In)
- MISO(Master In Slave Out)
- SCKL(Serial Clock)
- SS(Slave Select)
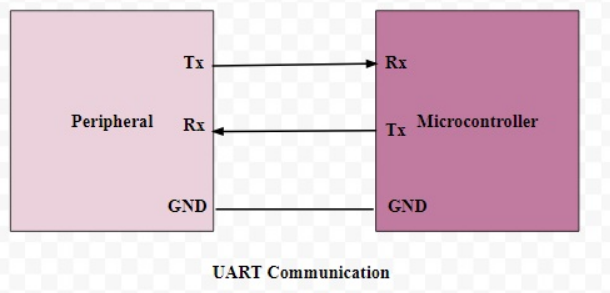
3. uart : Universal Asynchronous Reception and Transmission
- full duplex mode, asynchronous
- 20 kbps @ 15m
- uses 2 wires(Tx, Rx)
reference : https://www.nextpcb.com/blog/spi-i2c-uart
회로도 해석 능력(2)
ARM 코어 구조(3)
하드웨어 디버깅 능력(2) (GPIO 제어 능력)
- 오실로스코프 사용 방법(1)
- 테스터기 사용방법(1)
Basic knowledge about electricity.
- DC(Direct Current)/AC(Alternating Current)
- Inverter, Converter
- What is Ground in eletricity?
운영체제가 있는 임베디드
free RTOS(취향에 따라 4순위 정도)
리눅스
- 컴파일 방법, gcc 사용법(1)
- 크로스 컴파일 개념(1)
- makefile 작성방법(1)
- 라이브러리 작성방법(2)
- 드라이버 구현 방법(1)
- 커널 컴파일 방법(1)
- 커널 포팅 방법(1)
- vi edit 쓰는 방법(3)
- gdb 쓰는 방법(4)
- path 설정방법(2)
- tcp, socket 통신 구현(1)
- 시리얼 통신 구현(1)
Reference
From OJ Tube
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.